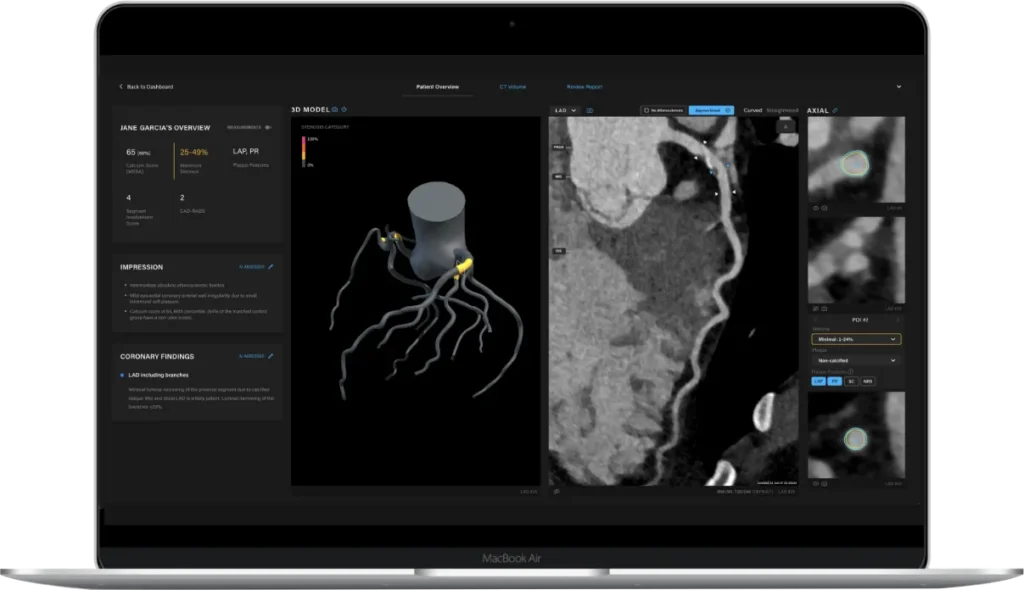
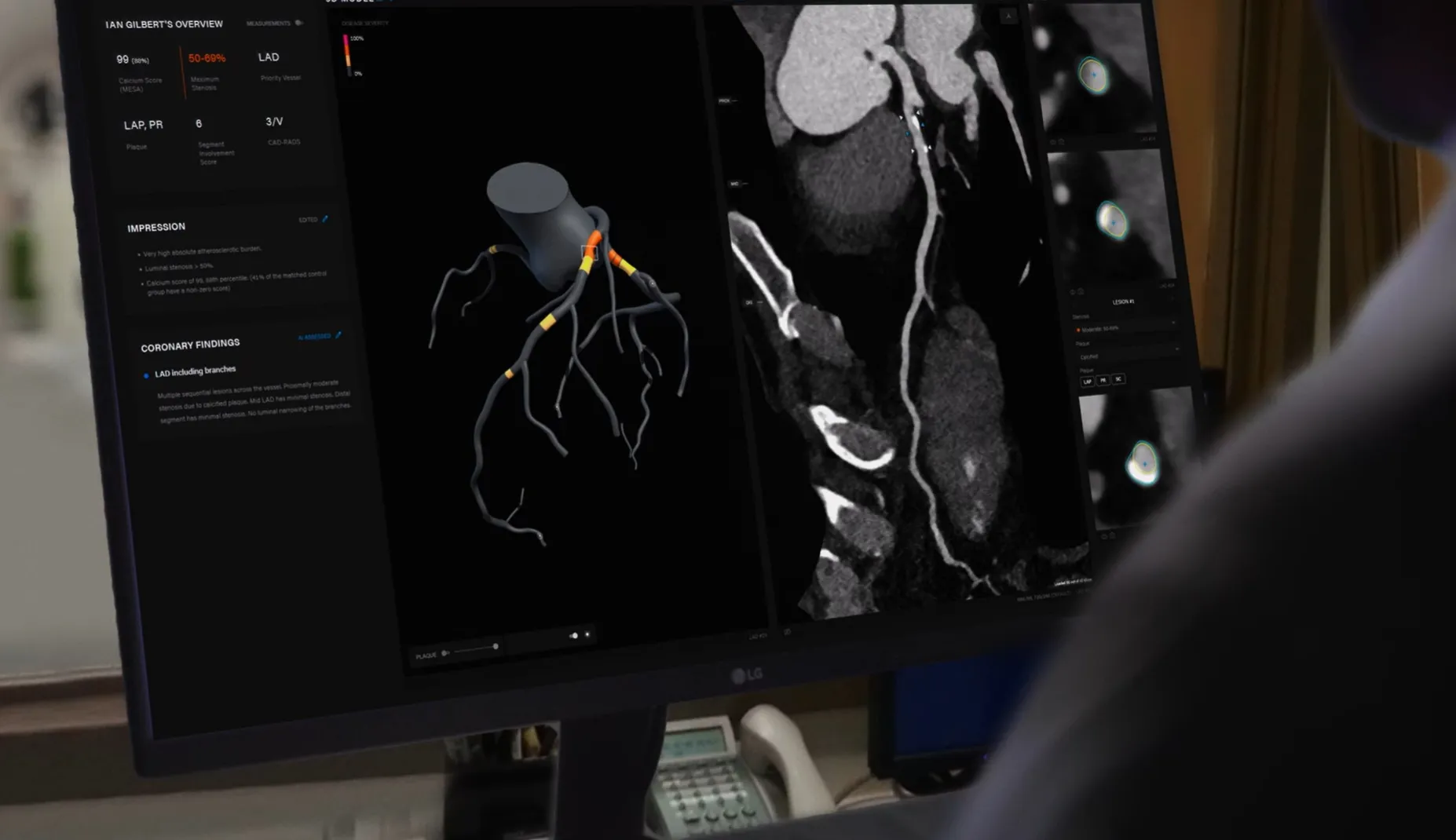
The key to scan analysis is the segmentation of the inner and outer walls of the coronary arteries. In this process, we identify and track the centerlines of the arteries.
Two convolutional neural network (CNN) based deep learning models are used to extract centerlines: a coronary artery seed detection algorithm and a centerline tracking CNN. Of importance, tracked arteries terminate at the detected aorta to eliminate false positives. Following centerline extraction, vessel wall segmentation projects the original CT scan into straightened multiplanar reprojection (sMPR) relative to each coronary artery.
To maximize the analysis of coronary artery disease indicators, stenosis is estimated by assessing the relative surface area of lumen cross-sections relative to a healthy reference, determined by identifying disease-free areas of the vessel proximal and distal to the lesion. Plaque features such as low attenuation plaque (LAP), positive remodeling and spotty calcification are detected by analyzing the spatial and radiometric characteristics in the region between the inner/lumen and outer walls of extracted coronary arteries. Plaque volume measurements are calculated by identifying voxels that are within the target Hounsfield Unit (HU) ranges and are spatially located between the inner/lumen and outer wall of the coronary arteries.
The algorithm has been built from access to thousands of scans from world-renowned medical institutes in the US, Australia and Canada for impressive accuracy.
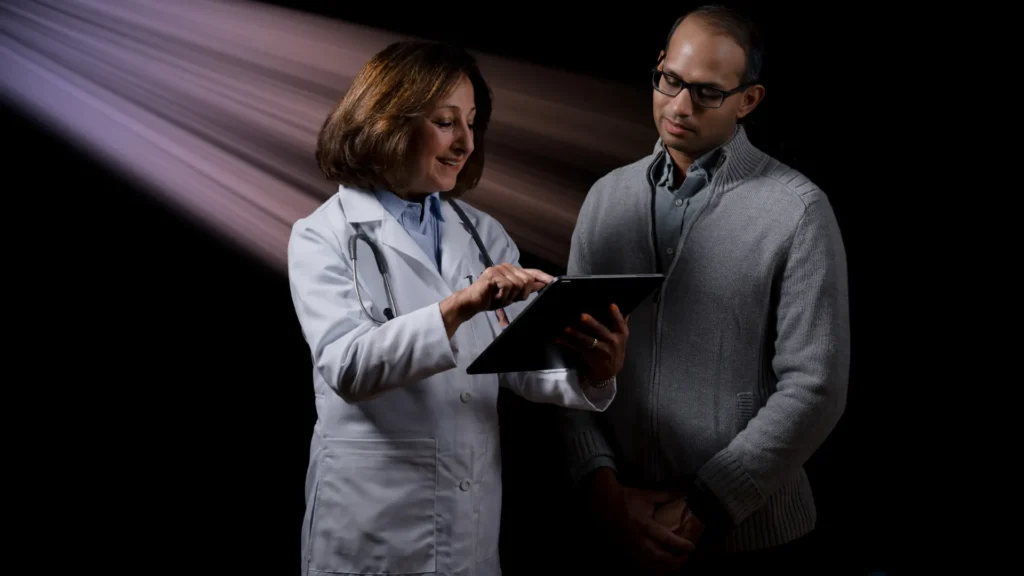
Physician-led, AI-based CCTA analysis coupled with an intuitive and easy-to-use clinical reporting platform can save physicians valuable time that can be used to educate, engage and collaborate with patients instead.
Rapid assessment. Accurate diagnosis.